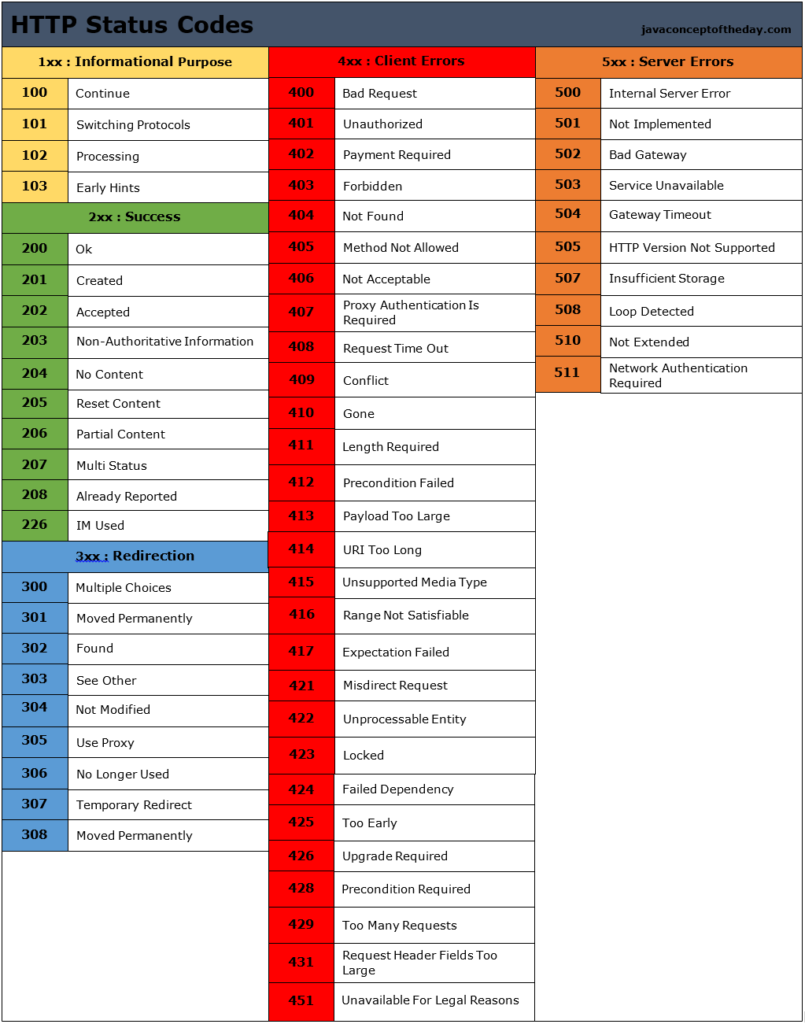
Status codes are essential for web communication. They inform browsers and users about the result of their requests.
Understanding these codes is crucial for anyone managing a website or developing web applications. Status codes indicate whether a request has succeeded, failed, or requires further action. They help diagnose issues and improve user experience. In this blog, we will explore the different types of status codes and what they mean.
This knowledge can help you quickly identify and fix problems, ensuring your website runs smoothly. Ready to decode the mysteries behind these numbers? Let’s dive in and see how status codes keep the web functioning seamlessly.
Introduction To Http Status Codes
Welcome to the world of HTTP Status Codes. These codes are essential for web communication. They help browsers and servers talk to each other. Understanding them is crucial for developers and site owners.
What Are Http Status Codes?
HTTP Status Codes are numbers that indicate the status of a web request. They are three-digit codes. They show if a request was successful, failed, or needs more action. For example, code 200 means success. Code 404 means the page is not found. Each code gives specific information about the web request.
Importance Of Status Codes
Status Codes are vital for web development. They help diagnose problems on a website. Knowing the right codes can save time and effort. They also improve user experience. If a page is not found, a 404 code tells the user right away. This helps in troubleshooting and fixing issues quickly.
Search engines also rely on these codes. They use them to understand how a website is performing. A site with correct status codes is easier to index. This can improve the site’s ranking in search results. So, knowing and using these codes is important for SEO.
1xx Informational Responses
Understanding HTTP Status Codes is essential for web developers and site owners. These codes are the server’s response to the browser’s request. Let’s dive into the 1xx Informational Responses, which indicate that the request has been received and is being processed.
Meaning Of 1xx Codes
The 1xx status codes are informational. They tell the client that the server has received the request and is continuing to process it. These codes are not final responses. They are just a notification.
Common 1xx Status Codes
There are a few 1xx status codes you might encounter. Here are the most common ones:
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 100 Continue | The server has received the request headers. The client should continue to send the request body. |
| 101 Switching Protocols | The requester has asked the server to switch protocols. The server is acknowledging that it will do so. |
| 102 Processing | The server has received the request and is processing it. This is used to prevent the client from timing out. |
2xx Success Responses
The ‘2xx Success Responses’ indicate that the request was successfully received, understood, and accepted. These status codes are a sign that everything went right with the web request. They reassure the user that the operation was completed without issues.
Meaning Of 2xx Codes
2xx status codes reflect successful interactions between the client and the server. They mean the server has fulfilled the client’s request. These responses confirm the smooth processing of the requested operation.
Common 2xx Status Codes
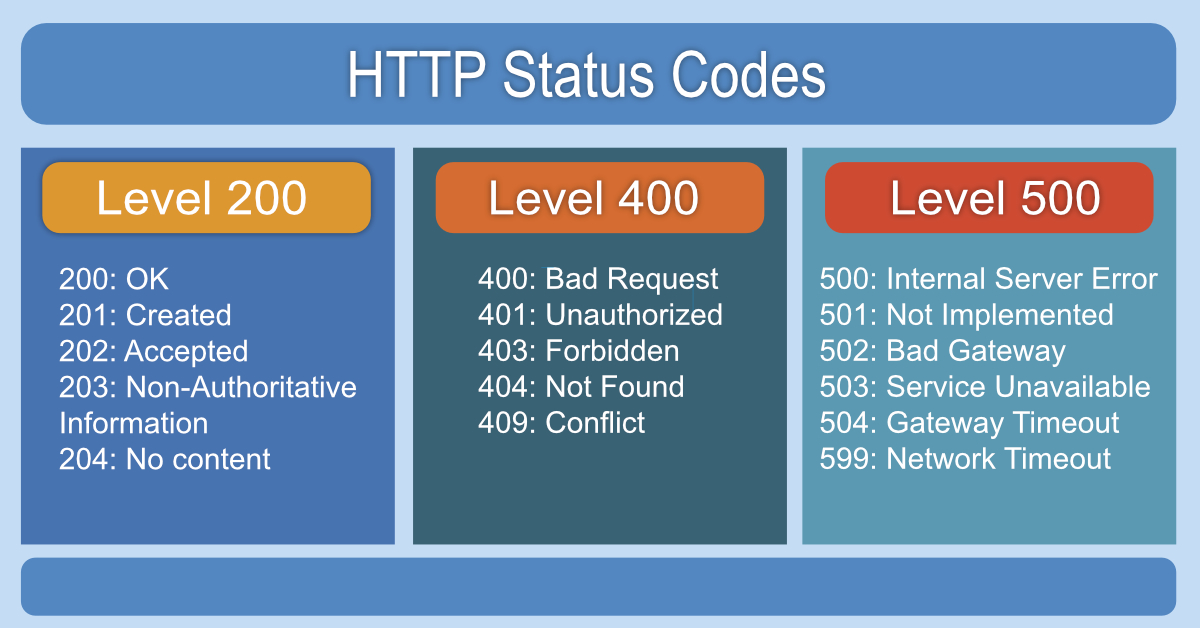
200 OK: This is the most common success code. It means the request was successful, and the server delivered the requested resource.
201 Created: This code indicates that a new resource has been successfully created. The server also provides the location of the new resource.
202 Accepted: This code means the request has been accepted for processing. The processing, however, is not completed yet.
204 No Content: This status code means the server successfully processed the request, but there is no content to return.
206 Partial Content: This code indicates that the server is delivering only part of the requested resource. This is often used for downloading files in chunks.
3xx Redirection Responses
In the realm of HTTP status codes, the 3xx series plays a crucial role. These codes indicate that further action is needed to complete the request. They primarily deal with redirection. This means the requested resource has moved to a new URL.
Meaning Of 3xx Codes
The 3xx status codes signify redirection. This means that the client must take additional steps. Typically, this involves following a different URL. These codes ensure a smooth browsing experience. They guide users and search engines to the correct location.
Common 3xx Status Codes
Several 3xx status codes are frequently encountered. Each serves a unique purpose. Here are the most common ones:
301 Moved Permanently: This code signals a permanent redirection. The resource has a new URL. Users and search engines should update their links.
302 Found: This code indicates a temporary redirection. The resource resides temporarily under a different URL. Future requests should use the original URL.
303 See Other: This code directs the client to retrieve the resource at another URL. Typically, it follows a POST request.
304 Not Modified: This code tells the client that the resource has not changed since the last request. The client can use the cached version.
307 Temporary Redirect: This code is similar to 302. It indicates a temporary redirection. The request method should not change.
308 Permanent Redirect: This code is similar to 301. It signals a permanent redirection. The request method should remain the same.
4xx Client Error Responses
In the world of web development, status codes play a critical role in communication between the client and the server. One of the most common categories is the 4xx Client Error Responses. These codes indicate that the client has made an error. This section will explain the meaning of 4xx codes and highlight some of the most common 4xx status codes.
Meaning Of 4xx Codes
The 4xx status codes signify that an error has occurred on the client-side. This means the request sent by the client has an issue. The server cannot process it because of this error. The error might be due to a malformed request or an unauthorized access attempt.
These errors are important because they help identify issues in the client’s request. Web developers can use this information to debug and improve user experience.
Common 4xx Status Codes
| Status Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 400 Bad Request | The server could not understand the request due to invalid syntax. |
| 401 Unauthorized | The client must authenticate itself to get the requested response. |
| 403 Forbidden | The client does not have access rights to the content. |
| 404 Not Found | The server cannot find the requested resource. |
| 408 Request Timeout | The server timed out waiting for the request. |
Understanding these common 4xx status codes is essential for troubleshooting and improving web applications. Below are some detailed explanations of each:
- 400 Bad Request: This error occurs when the server cannot process the request due to a client-side error. It might be because of incorrect syntax or invalid parameters.
- 401 Unauthorized: This status means the client needs to authenticate. Without proper authentication, access to the resource is denied.
- 403 Forbidden: This indicates that the client’s identity is known, but they do not have permission to access the resource.
- 404 Not Found: The server cannot find the requested resource. It often means the URL is incorrect or the resource has been moved.
- 408 Request Timeout: The server did not receive a complete request in time. This error is often due to a slow connection or network issues.
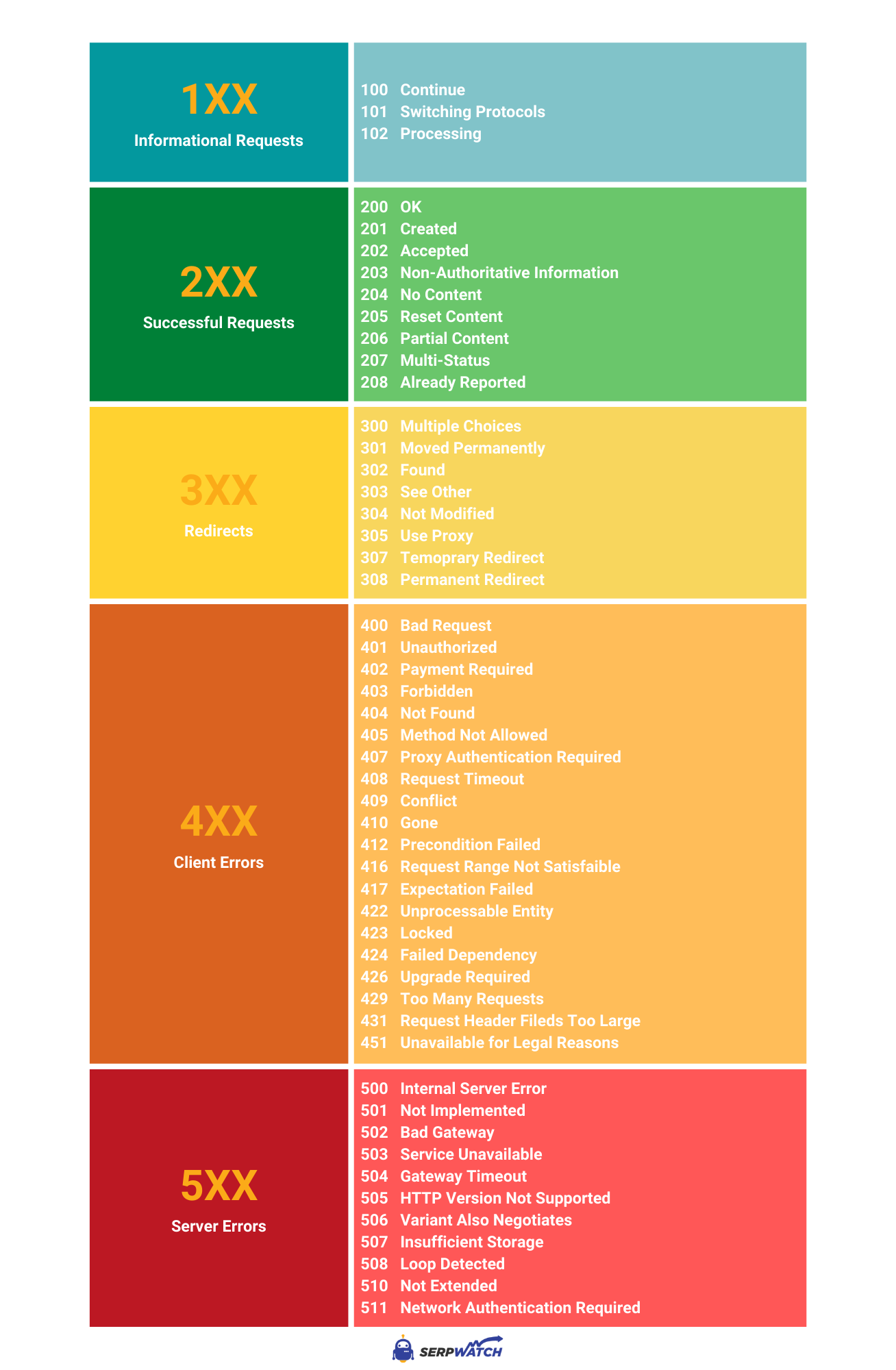
Credit: serpwatch.io
5xx Server Error Responses
Understanding server error responses is crucial for web developers and site owners. The 5xx status codes indicate server errors. These errors occur when the server fails to fulfill a valid request. They can affect user experience and site performance. Let’s dive into the details of 5xx server error responses.
Meaning Of 5xx Codes
The 5xx status codes signal issues with the server. They show that the server is aware it has encountered an error. These errors prevent the server from completing the request. They often indicate temporary issues or serious server problems.
Common 5xx Status Codes
Several common 5xx status codes can impact your website. Here are a few key ones:
- 500 Internal Server Error: This is a generic error message. It means the server encountered an unexpected condition.
- 502 Bad Gateway: This error indicates the server received an invalid response. The invalid response comes from an inbound server.
- 503 Service Unavailable: This means the server is currently unable to handle the request. Often, the server is down for maintenance or overloaded.
- 504 Gateway Timeout: This error occurs when one server does not get a timely response. It happens from another server it was accessing.
- 505 HTTP Version Not Supported: This error states the server does not support the HTTP version. The HTTP version used in the request is not supported.
Knowing these status codes helps in troubleshooting server issues. It also aids in maintaining a smooth user experience on your website.
Less Common Http Status Codes
HTTP status codes are essential for web communication. Most people are familiar with the common ones like 404 and 500. But there are many lesser-known status codes. These codes are rarely used but can be very useful in specific situations.
Rare 1xx Codes
The 1xx status codes are informational responses. They indicate that the request has been received and is being processed.
- 100 Continue: This code means the server has received the request headers. The client should continue to send the request body.
- 101 Switching Protocols: This code means the server is changing protocols as requested by the client.
- 102 Processing: This code is used in WebDAV applications. It indicates that the server has received and is processing the request, but no response is available yet.
Rare 3xx Codes
The 3xx status codes are redirection messages. They tell the client that further action is needed to complete the request.
- 305 Use Proxy: This code means the requested resource must be accessed through a proxy specified in the response.
- 306 Switch Proxy: This code is no longer used but was meant to tell the client to use a different proxy.
- 307 Temporary Redirect: This code means the requested resource has been temporarily moved to a different URI.
Credit: restfulapi.net
Practical Use Of Status Codes
Status codes are essential for web communication. They inform clients about the status of their requests. Understanding them helps in troubleshooting and efficient web development.
Troubleshooting With Status Codes
Status codes help identify issues quickly. For instance, a 404 Not Found error means the URL is incorrect. Fixing this can involve checking the URL or ensuring the resource exists.
A 500 Internal Server Error indicates a server-side problem. It might be due to a misconfiguration or a temporary overload. Checking server logs can help identify the root cause.
| Status Code | Meaning | Common Cause |
|---|---|---|
| 200 | OK | Request succeeded |
| 301 | Moved Permanently | Resource moved to a new URL |
| 403 | Forbidden | Access denied |
Best Practices For Developers
Developers should handle status codes properly. This ensures smooth user experiences and effective debugging. Consider these best practices:
- Always return the correct status code. For example, use 200 for success and 404 for missing resources.
- Use 301 redirects for moved resources. This helps with SEO and maintains user access.
- Log all 500 errors. Analyzing logs helps fix server issues promptly.
Implementing these practices helps maintain a reliable and user-friendly web environment.

Credit: www.infidigit.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Status Codes?
Status codes are numerical codes returned by servers to indicate the outcome of a client’s request. They help identify whether a request was successful, redirected, or resulted in an error.
Why Are Http Status Codes Important?
HTTP status codes are crucial for diagnosing issues and ensuring proper communication between clients and servers. They help developers understand what went wrong or confirm successful operations.
What Does A 404 Status Code Mean?
A 404 status code means the requested resource could not be found on the server. It indicates the server cannot locate the requested URL.
How Do I Fix A 500 Status Code?
A 500 status code indicates a server error. To fix it, check server logs for errors, verify server configurations, and ensure scripts are functioning correctly.
Conclusion
Understanding status codes is crucial for web developers and site managers. They help diagnose issues quickly. Knowing these codes enhances site performance. It improves user experience and SEO ranking. Regularly check status codes to maintain a healthy website. This practice ensures smooth operation and better search engine visibility.
Stay informed and keep your site running efficiently. Your users will appreciate the seamless experience.
Ms.Sultana brings over 16 years of expertise working with global Clients by providing different skills and Services. For the last 5 years working as an Affiliate marketer, specializing in high-ticket campaigns that drive exponential growth. She holds a degree in Computer Science and Engineering as well as achieved many more skills certificates from different institute/academies/Platform. As part of the Elite Global Marketing team, Sultana has helped clients generate millions in revenue through strategic partnerships, innovative funnels, and data-driven insights.